Mowat -Wilson syndrome is a rare, genetic developmental disorder with a variety of symptoms. In addition to facial, intestinal and genital anomalies, the genetic defect also includes heart defects and brain development disorders. The previously incurable disease can only be treated symptomatically.
What is Mowat Wilson Syndrome?
Mowat -Wilson syndrome is a relatively young disease. The clinically diverse phenomenon was first described by Mowat and Wilson in 1998. In addition to developmental disorders, microcephaly and the symptom complex of Hirschsprung ‘s disease characterize the clinical picture. A genetic defect is considered to be the cause of the disease. See fun-wiki for What is Kartagener Syndrome used for.
Overall, the symptoms are extremely varied. Little research has been done on this rare disease so far. As a result, few treatment options are currently available. There is no definitive prevalence because the disorder has rarely been diagnosed, if at all, into the 21st century. A total of around 200 patients with the syndrome are currently documented.
Causes
A gene mutation causes Mowat-Wilson syndrome. According to current research, the ZFHX1B gene is the disease-causing gene. The causative gene defect is said to be in the chromosome region 2q22. The affected gene is around 70 kb in size and is made up of a total of ten exons of 1214 amino acids. This gene encodes the protein SIP1, which acts as a transcription modulator and is involved in embryogenesis.
The embryogenesis of those affected is therefore disturbed. The disease-causing anomalies in the gene can correspond to a complete deletion, to a repositioning, or to a sequential anomaly. The genetic defect is passed on in the autosomal dominant inheritance. A defective allele on the two homologous chromosomes is sufficient for the transmission of the hereditary disease.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
The symptoms of Mowat-Wilson syndrome correspond to a complex developmental disorder and are clinically diverse. Cardinal symptoms include cerebral seizures and microcephaly. Such microcephaly occurs as a result of early hardening of all cranial sutures and constricts the brain during the growth phase. Because of this, patients are affected by mental retardation. In addition, facial anomalies are often present, often giving the patient an eagle-like profile.
These abnormalities may correspond, for example, to large, deep-set eyes, horizontally arched eyebrows, pinna abnormalities, attached earlobes, and a prominent chin. In 90 percent of cases, those affected suffer from epilepsy. Mental development is severely delayed and language development is often completely absent. The motor development of the patients is also slowed down.
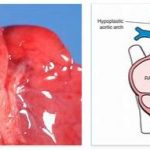
With normal birth dimensions, secondary short stature often occurs. Malformations of the urethra may be present. Congenital heart defects or malformations of the genitals are also conceivable. In addition, neuronal anomalies of the intestinal wall plexus occur, which are characteristic of Hirschsprung disease.
Diagnosis & course of disease
The diagnosis of Mowat-Wilson Syndrome cannot be made on the basis of mere examinations, but requires analysis of the genetic material. From the patient’s genomic DNA, the laboratory amplifies exons two to ten of the ZFHX1B gene. This amplification takes place using PCR. This material and the intron-exon splice sites are analyzed using DNA sequencing.
Each exon of the ZFHX1B gene is examined for deletion and duplication using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. This time-consuming procedure takes around three weeks and, unlike simply examining the patient, can enable an unequivocal diagnosis to be made. In most cases, the affected person’s DNA is also sequenced and analyzed along with that of their parents.
The course of the disease is highly dependent on the form of the genetic abnormality and the extent of the deletion or repositioning of parts of the chromosome. Definitive forecasts can hardly be made because of the few cases of illness that have been documented to date. However, early diagnosis and subsequent therapy probably have a favorable effect on the prognosis.
Complications
The Mowat-Wilson syndrome leads to serious symptoms and complications in the patient, which significantly reduce life expectancy and quality of life. As a rule, the everyday life of the patient is also significantly restricted and those affected are dependent on the help of other people in their everyday life.
Furthermore, there is mental retardation, in which it is not uncommon for relatives and parents to suffer from psychological complaints or depression. In most cases, those affected also suffer from cramps and reduced resilience. Various deformations of the face also occur and epilepsy occurs.
Language development is also significantly delayed, so that in adulthood there are considerable difficulties in communicating with the patient. A heart defect and short stature also occur. The heart defect can lead to spontaneous cardiac death, so that the life expectancy of those affected is limited by Mowat-Wilson syndrome.
There is no cure for Mowat Wilson Syndrome. However, the various complaints can be limited and treated so that the person concerned has a tolerable everyday life. Although there are no complications, positive treatment is not always possible.
When should you go to the doctor?
Although the Mowat-Wilson syndrome cannot be cured with the current legal and medical possibilities, a significant alleviation of the symptoms can be achieved by treating the symptoms that occur. The earlier a diagnosis can be made, the better the patient’s treatment options are normally. Consultation with a doctor is necessary if there is a developmental disorder in the growing child.
If individual abnormalities appear in direct comparison to peers, a doctor is needed. The observations should be discussed with him so that the state of health can be assessed. A learning disability, memory disorders, a speech delay or peculiarities of the movement sequences must be presented to a doctor. If cramps, pain or abnormal posture occur, a doctor should be consulted. Malformations or abnormalities of the face indicate a condition that requires treatment.
A visual defect or abnormalities in the facial features must be clarified by a doctor. Slowed thinking processes or movements are signs of a disorder and should be investigated. If cardiac arrhythmia occurs, there are problems with excretion or if there are irregularities in the ability to react or perceive, a doctor should be consulted. Behavioral abnormalities, vegetative disorders or peculiarities of the complexion must be examined by a doctor.
Treatment & Therapy
The Mowat-Wilson syndrome is so far incurable. The symptomatic treatment options are also limited. Drug therapies are usually used to treat seizures. Antiepileptic drugs show the greatest effectiveness in this context. Some of the symptomatic malformations can be corrected surgically. The symptoms of Hirschsprung’s disease in particular should be corrected as early as possible, since otherwise sepsis or migratory peritonitis could develop.
The symptomatic therapy of Mowat-Wilson syndrome is primarily intended to improve the quality of life of those affected. With this goal, mental and motor retardation can also be counteracted. Under certain circumstances, speech therapy can help with language development, which often does not occur in Mowat-Wilson syndrome without supportive therapeutic measures. Physiotherapeutic and ergotherapeutic treatments can meanwhile counteract the delayed development of motor skills.
The Mowat-Wilson syndrome is often an almost unimaginable psychological burden for the parents of an affected person. For this reason, the parents of the patients are often supported by psychotherapists. Medical research is currently concerned with gene therapy approaches that are intended to heal genetic defects in the future. The defective ZFHX1B gene of those affected can soon be replaced, which may make the disease curable.
Outlook & Forecast
Mowat-Wilson syndrome can be treated well nowadays. Life expectancy and quality of life are based on the type and severity of the congenital malformations. For mild abnormalities that don’t affect the heart, people can live into adulthood.
Seriously ill patients usually die during childhood or adolescence as a result of the disease. Typical causes of death are myocardial infarction or the characteristic HSCR diseases. The cerebral seizures often lead to death during the first years of the child’s life. The rare syndrome can be treated symptomatically, allowing patients to lead a symptom-free life, at least temporarily.
However, in the long term, Mowat-Wilson syndrome does not offer a positive prognosis, since the various malformations and anomalies lead to progressive deterioration in health and eventually to death. The prognosis about life expectancy and the course of the disease is usually made by the responsible specialist. This is usually a neurologist or a doctor who specializes in genetic diseases. Depending on the symptoms, the diagnosis of the disease can be difficult, which is why the Mowat-Wilson syndrome is often not diagnosed before the disease is well advanced.
Prevention
Since Mowat-Wilson syndrome is a complex developmental disorder with a genetic cause, the phenomenon can hardly be prevented. However, couples who are planning a family can have their DNA sequenced in order to assess their personal risk of passing on genetic defects.
Aftercare
In most cases, those affected with Mowat-Wilson syndrome have little or no follow-up care available, since this is a genetic disease. Therefore, those affected should ideally consult a doctor at an early stage so that there are no further symptoms or complications that can have a negative impact on the life expectancy and quality of life of the person affected.
As a rule, self-healing cannot occur, so that a doctor should be consulted at the first signs and symptoms of the disease. If you wish to have children, genetic testing and counseling can be useful to prevent the syndrome from recurring in the offspring. As a rule, those affected by Mowat-Wilson syndrome are dependent on taking various medications.
These should always be taken in good time and in the right dosage to alleviate the symptoms. In the case of children, it is primarily the parents who should control the intake. Physiotherapy measures are also necessary in many cases, although some of the exercises can also be carried out at home. It cannot be universally predicted whether the life expectancy of those affected will be reduced as a result of Mowat-Wilson syndrome.
You can do that yourself
Unfortunately, since there are currently no cures for Mowat-Wilson syndrome, the priority is to improve the child’s quality of life.
In many cases, logopedic therapy started early can counteract the delayed language development and ensure significant success in language development. In addition, intensive physiotherapeutic and ergotherapeutic measures ensure better motor and mental development. In addition to the measures prescribed by the doctor, it is definitely advisable to deal with the topic yourself and continue the therapy at home.
Caring for a disabled child is an enormous burden, especially for the parents, but also for any siblings, which can affect family life and, ultimately, the quality of care. It is therefore extremely important that the parents in such cases seek psychotherapy in good time, which will give them more strength in the long term by learning methods for relaxation and conflict resolution.
It should also be borne in mind that those affected are entitled to stand-in care for up to six weeks each year, for which the care insurance company will bear the costs. There are already facilities where intensive care is given during the day while relatives can relax on excursions. This can be a great help, especially with siblings.