Darier’s disease is an autosomal dominant hereditary skin disease that manifests itself in disturbed keratinization of the epidermis, fingernails and hair follicles. This keratinization disorder is also known as keratoderma and is very rare in congenital syndromes. The name Darier’s disease goes back to the French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier, who first described the disease in 1899.
What is Darier’s disease?
About 1 in 50,000 people are affected by Darier’s disease. The syndrome is also known as Darier’s disease and follicular dyskeratosis. The autosomal dominant inherited keratinization disorder progresses slowly and forms reddish-brown to dirty-gray papules. See lawfaqs for Definitions of Cardiomyopathy.
These coalesce into larger plaques over time, eventually becoming papillomatous growths covered with fatty crusts or oozing. Affected patients often suffer from skin infections, especially from the herpes simplex virus. Overexposure to UV rays or sunburn can trigger or worsen the uncomfortable skin changes.
Causes
The skin disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This often leads to spontaneous mutations affecting a calcium ATPase (ATP2A2) on chromosome 12 (gene locus 12q24.11). This plays an important role in the distribution of calcium in the cytoplasm of skin cells. The mutation causes a disruption in protein production, which in turn causes a disruption in the differentiation of skin cells. This causes the keratinocytes to die.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
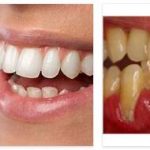
The disease can be recognized externally by scaly, crusted papules that are reddish or greyish in color and often confluent. They usually occur in the middle of the face, on the hairy head, in the anogenital region or in the posterior and anterior axillary line. The abnormal keratinization of the skin produces the characteristic punctiform interruptions on the papillary ridges of the balls of the fingers and toes.
A brownish callus forms on the backs of the feet and hands. On the other hand, whitish papules often develop on the mucous membranes of the hard palate and cheeks. Occasionally, these can also be found on the rectum and genital mucous membranes. Fingernails and toenails can be streaked with furrows and reddish and whitish streaks.
Irritation caused by sweat, UV light, moisture or friction can damage the skin or cause itching. In addition, bacterial superinfections can occur and cause an unpleasant odor in the affected areas. Sometimes even cystic bone changes occur. There are also special clinical forms that arise, for example, in connection with fever and heavy sweating.
Diagnosis & course of disease
Darier’s disease occurs mostly in children and is more common in the peri-pubertal period. About 70 percent of patients are between 6 and 20 years old when the skin disease first occurs and the disease peaks during puberty. Typical of the syndrome is the unsteady course, in which flare-ups and phases without symptoms alternate.
A complete resolution of the symptoms is extremely rare. The syndrome occurs in varying degrees of severity. The diagnosis is made by examining the papules and looking at the clinical picture. One of the features is papillomatosis, that is, an enlargement and coarsening of the papillae of connective tissue protruding into the epidermis. They thicken and therefore result in an uneven skin surface.
Hyperkeratosis, i.e. excessive cornification, is also part of the clinical picture, as is premature single-cell cornification (dyskeratosis). Various main and secondary criteria are used for the diagnosis. The main criteria include the characteristic appearance of the skin, itching and the individual and family medical history. Children in particular are often wrongly diagnosed with neurodermatitis, since Darier’s disease often occurs in the form of dry skin at a young age.
Complications
Patients with Darier’s disease primarily experience skin problems. This is reddish and often affected by itching. Papules or pustules can also form and significantly reduce the aesthetics.
Especially in the middle of the face, the complaints and symptoms can be very unpleasant and thus lead to inferiority complexes or a severely reduced self-esteem. Darier’s disease can lead to teasing or bullying, especially in children. Most patients are ashamed of the symptoms. Fever and, not infrequently, sweating can also occur.
If the disease is not treated, changes can also occur in the bones, which have a very negative effect on the patient’s quality of life. Furthermore, Darier’s disease also affects the fingernails. With the help of antibiotics and various creams, the symptoms of Darier’s disease can be significantly reduced and limited.
Complications, as a rule, arise only if the disease is not treated. In most cases, the treatment itself leads to a positive course of the disease and there is no reduction in life expectancy.
When should you go to the doctor?
Changes in the appearance of the skin are signs of a health impairment that should be clarified by a doctor. If the skin becomes scaly, crusting or discolored, it is advisable to consult a doctor. If the symptoms persist for several weeks or increase in intensity, you need to consult a doctor. Characteristic of Darier’s disease is the onset of irregularities on the face and the top of the head. So that the cause can be clarified and medical care can be provided at an early stage, a doctor should be consulted as soon as the first symptoms appear. Growths, knots and poplars should be presented to a doctor.
Since it is a genetic disease, the first symptoms appear in childhood during the natural development process. Parents are therefore encouraged to present their offspring to a doctor as soon as the optical changes develop in direct comparison to children of the same age. Action is required if the skin feels itchy or feels tight. If open wounds develop, the affected person needs sterile wound care because there is a risk of sepsis. In severe cases, blood poisoning can lead to premature death and if the wound shows any abnormalities, it should be examined by a doctor as soon as possible. If emotional or mental problems appear due to the optical features, a doctor’s visit is recommended.
Treatment & Therapy
Since Darier’s disease is a chronic disease that goes back to an error in the genetic material, a complete cure is not possible. However, there are various treatment methods that can alleviate the symptoms. External corticosteroids can be used to treat acute symptoms during a flare-up in the short term.
In the case of a bacterial superinfection, antibiotics and antiseptic baths are also used. In addition, creams with a high water content ensure pleasant cooling in this situation. In general, it is advisable to use ointments regularly to prevent the skin from drying out. Zinc ointments can help in acute phases of inflammation that are accompanied by weeping. Powders are also helpful because they are gentle on the skin and do not cause new wounds to develop.
For internal use, drug treatment is often initiated. Doctors recommend taking retinoids, which are usually used to treat psoriasis and acne. They are available in capsule form as well as in creams, gels or as solutions. Since this can lead to side effects and some retinoids should not be taken by pregnant women, the treatment should be coordinated with a doctor in advance.
Outlook & Forecast
Darier’s disease offers a relatively good prognosis. The disease can be treated with medication and is only noticeable externally. In addition, the symptoms usually only occur in one season. Life expectancy is not restricted by the condition, since the individual symptoms can be completely cured as part of the therapy.
Late effects are usually not to be expected. During an acute flare-up, well-being is limited by itching and dandruff. However, antibiotics and antiseptics improve symptoms. In addition, home remedies such as cooling pads or soothing ointments from nature can quickly relieve even acute symptoms.
The prognosis is made by the dermatologist or an internist. He consults the previous course of the disease, the intensity of the relapses and the therapy measures to give the patient an outlook. This usually makes it relatively easy to assess how Darier’s disease will progress in the future. A causal treatment is not yet available. Due to the good treatment options, the overall prognosis is good and there are few limitations for those affected if treatment is given early.
Prevention
While there is no way to prevent the inherited skin condition, there are certain precautions you can take to better manage the symptoms. When choosing care products, fragrances, colorings and preservatives should be avoided, as these can worsen the condition of the skin.
The same sometimes applies to greasy ointments that cause heat to build up. Dirt and bacteria often lead to skin inflammation, which is why good personal hygiene is particularly important for those affected. In addition, foods high in calcium can irritate and affect the skin. Other factors that can aggravate the disease are lack of sleep, stress, excessive sunbathing and alcohol consumption.
Aftercare
In most cases, the options and measures for direct follow-up care are significantly limited in Darier’s disease and are often not even available to those affected. Therefore, ideally, the patient should see a doctor very early on to prevent the onset of other ailments and complications. It cannot heal on its own.
If there is a desire to have children, genetic testing and counseling can be useful to prevent the recurrence of Darier’s disease in the offspring. In many cases, the symptoms can be significantly alleviated by taking various medications and using creams.
If possible, no alcohol should be drunk while taking antibiotics. Furthermore, regular checks by a dermatologist are very important for Darier’s disease, so that other damage can be recognized and treated early. The disease itself usually does not reduce the life expectancy of the patient.
You can do that yourself
Since there is no way to completely cure Darier’s disease, measures must be taken to provide relief for the person concerned. Careful attention should be paid to ingredients, especially when it comes to skin care products. Dyes, fragrances and preservatives should not be included, as these can have a negative effect on the condition of the skin. You should also be careful with greasy ointments, as they cause heat to build up.
Dirt, bacteria and fungi can cause skin inflammation, which is why adequate personal hygiene is essential for those affected. Nevertheless, it is important to maintain personal hygiene in moderation in order to promote the skin’s natural protective mechanisms. Dairy products often contain large amounts of calcium, which is irritating to the skin. In a direct comparison, plant-based substitute products have a high vitamin E and C content, which can significantly improve the complexion. Smoking, stress, lack of sleep and excessive alcohol consumption and poor diet can also be associated with risks.
All medications prescribed by the attending physician should be taken within the prescribed period. Prescribed medicines can, among other things, have side effects affecting the psyche, which (if any) must be investigated immediately. In addition, places where a lot of fine dust and large amounts of exhaust gases are produced should be visited less often or replaced with an alternative.