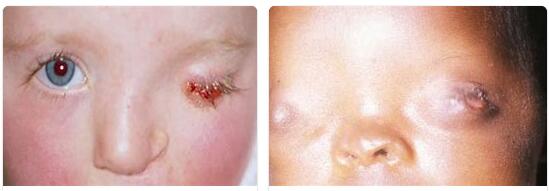
The Anophthalmus is characterized by the absence of one or both eyes plants. In many cases it is a symptom of a hereditary disease. It can also occur after a serious eye disease or an enucleation.
What is anophthalmos?
In the case of congenital anophthalmos, the child is born blind with no eye appendages. The anophthalmos also affects the rest of the skull growth.
According to sciencedict, anophthalmos represents the absence of the eye primordia. The term anophthalmia can also be used as a synonym for anophthalmos . There is both unilateral and bilateral anophthalmia. Anophthalmos is rare and often occurs in the context of congenital diseases. The congenital diseases can be hereditary or caused by disorders during pregnancy .
Zu The congenital diseases in which anophthalmos may develop include the so-called Pätau syndrome , holoprosencephaly or Fraser syndrome . Anophthalmia can also develop as a result of infections, tumors or trauma to the eyes. In some cases, the eyeballs must be surgically removed as part of a serious eye condition. This procedure is also known as enucleation.
Causes
The causes for the development of anophthalmos are diverse. It should be noted that eye development is a very complicated process. The severity of the malformation also depends on the developmental state of the embryo in which the malformation begins. The critical phase of eye development takes place in the third to seventh week of pregnancy.
Disturbances during this period can lead to the complete absence of the eye systems. Sometimes, however, the higher components of the visual pathway are created up to the cerebral cortex. In this development phase , gene mutations , chromosomal changes or even intrauterine infections have a major influence on the development of the eye primordia.
Anophthalmias can develop, among other things, as part of a Pätau syndrome, a Fraser syndrome or holoprosencephaly. Patau syndrome is a hereditary disease in which there is a trisomy of chromosome 13. So here chromosome 13 is present three times instead of normally twice. In addition to various malformations, anophthalmos can also occur here.
Fraser syndrome is also hereditary and shows, in addition to many malformations, the lack of both eye anchors as a main symptom. Holoprosencephaly, in turn, is characterized by prenatal malformation of the face and forebrain. There are both genetic and environmental causes. Infections and environmental toxins play a role here. Subsequent diseases of the eyes such as infections, tumors or injuries can lead to the acquired forms of anophthalmia.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
In the case of congenital anophthalmos, the child is born blind with no eye appendages. The anophthalmos also affects the rest of the skull growth. It not only disrupts the development of the eye socket (orbit) and its contents. The facial skull in particular can no longer grow properly. Therefore further deformations mainly occur in the area of the face.
A facial asymmetry develops, which affects the entire chewing apparatus. Therefore, the changes in the face are directly related to the missing eye anchors. In the case of congenital anophthalmos, the primary treatment of glass-shell prostheses is therefore not possible. The other symptoms depend on the underlying disease. Anophthalmos can also result in psychological and psychosomatic complaints.
Diagnosis & course
Anophthalmia is defined as a lack of eye anlage and is therefore easy to determine. It is more difficult to diagnose the underlying disease. However, knowing whether it is congenital or acquired is critical to treating anophthalmos. By X-ray examinations the degree of malformation can be determined.
Complications
Anophthalmos can lead to very serious complications. In and of itself, anophthalmos is a serious complication because humans have been blind from birth. This leads to considerable restrictions in everyday life and in social life.
Blindness also usually leads to a shorter life expectancy because the patient cannot correctly identify and anticipate certain diseases or dangerous situations. The lack of eyes also leads to malformations in the face, as the skull can no longer grow without restrictions. The anophthalmos cannot be treated because the eyes cannot simply be replaced.
The patient therefore has to spend his entire life without eyesight, which can lead to depression and upset. For this reason, the treatment is mainly limited to cosmetic operations to remove asymmetries in the face. The empty eye socket can be filled with an artificial eye.
However, the treatments are not possible in children, as the dimensions of the face and eye socket change as they grow. With anophthalmos, it is not to be expected that the disease will go away without therapeutic help.
When should you go to the doctor?
Anophthalmos in the child is usually detected during pregnancy during a routine ultrasound examination. The attending physician can usually see the absence of one or both of the eye systems directly and will inform the parents of this immediately. The further treatment steps usually include consultations with specialists and other affected persons. Often the mother and father of the child take advantage of other therapy options. If the anophthalmos is not noticed immediately, it can be diagnosed at birth at the latest.
An immediate medical examination provides information about the treatment options. Usually the missing eyes can be replaced by an eye prosthesis. The eyesight itself is not restored with these facial cosmetic measures. However, further visits to the doctor are necessary, during which the prosthesis is repeatedly adjusted.
Whether the affected child needs medical assistance later in life depends on many factors. Therapeutic measures can be used to increase the self-esteem of the person affected and to accept the anophthalmos in the long term. Psychotherapeutic examinations are particularly necessary in cases in which the anophthalmia did not develop until later in life.
Treatment & Therapy
Facial cosmetics are used to treat anophthalmos. The eyesight cannot be established in this way. Missing eyes are replaced by an eye prosthesis. However, it makes a difference whether the anophthalmos is congenital or acquired. In congenital anophthalmos, the proportions change continuously while it is growing.
A prosthesis has to be adjusted over and over again. The artificial eye is made individually depending on the size of the eye socket. However, this has to be done constantly because the size of the eye sockets changes constantly as it grows. In very young patients in particular, the underdeveloped eyelid apparatus often cannot stabilize the position of the glass bowl.
Even slight mechanical stress, such as rubbing the eyes, quickly loosens the prosthesis and changes its position. Surgical interventions attempt to strengthen the lid apparatus in order to stabilize the position of the eye prostheses. This often turns out to be very complicated. For this reason, methods are being developed to stretch the conjunctival sac with a so-called tissue expander and thus stimulate it to grow.
However, these procedures are not yet fully developed. However, improvements could be achieved. If anophthalmos is acquired through illness or an accident, the growth is usually already complete, so that the dimensions of the eye sockets no longer change. So it is very easy to use a stable eye replacement here.
Outlook & forecast
With anophthalmos there is no prospect of an improvement in the health situation. A restoration of the eyesight or a functional artificial replica of the entire eye area is not given with the current medical possibilities. It is a genetic defect that cannot or must not be remedied either scientifically or for legal reasons.
A shortening of the normal life expectancy is not given with the anophthalmos. Nevertheless, various secondary diseases can lead to a deterioration in the general condition. The lack of sight contributes to difficulties in coping with everyday life. An independent life is almost impossible without help. There is a risk of mental and emotional problems. These have a negative impact on health. Stress and decreased self-esteem can lead to the development of fear of rejection.
In most cases, with therapeutic support, there are good prospects for coping with everyday conflicts, since one learns to deal with health impairments from birth. However, it can also lead to permanent mental disorders for which little or no relief is possible. In addition to the psychological stress, the insertion of an eye prosthesis can result in inflammation or damage to the surrounding regions. These also weaken general well-being.
Prevention
Prevention of congenital anophthalmos is usually not possible. Very often these are genetically determined diseases that lead to this malformation in the early phase of embryonic development. However, since certain environmental influences can also lead to deformities, smoking and alcohol should be avoided during pregnancy.
However, constant medical examinations during pregnancy are also important in order to rule out teratogenic diseases or to detect them in good time. Since diabetes is also a risk factor, a balanced diet and plenty of exercise are recommended.
Aftercare
Follow-up care cannot aim to prevent anophthalmos from recurring. This is because the disorder cannot be cured. Anophthalmos usually has genetic causes and is already present in newborns. In addition, accidents or serious illnesses can cause the typical symptoms.
Follow-up care should primarily make everyday life easier. In order to determine the extent of the impairment to the eyes, doctors carry out extensive examinations of the organ of vision. The extent of the disease can also be seen through x-rays. A missing eye is usually replaced by a prosthesis.
Since children are still growing, this cosmetic product should be adjusted regularly. Suitable facilities such as an eye socket are not always available. There are also challenges beyond appearance. The limited perception can be addressed in a therapy. It is about coping with everyday life as independently as possible despite the limited vision.
Many of those affected suffer from mental disorders as they get older. Stress and the fear of rejection can be reduced in psychotherapy. Sometimes discussions in a self-help group can also help. Follow-up care therefore primarily pursues cosmetic and emotional goals.
You can do that yourself
Since the anophthalamus is innate, the baby and later the toddler must be given special support right from the start, especially if the eyes are missing on both sides. One-eyedness is so well compensated by the brain that the adult person can lead a completely normal life. If there is a genetic defect on both sides, the child, and later the adult, must learn to lead the life of a blind person .
In the few cases in which the anophthalamus only develops in adulthood due to illness or accident, the patient will not be able to do without accompanying psychotherapeutic treatment . There are also self-help groups for the blind.
The parents of the “children without eyes” also offer a Germany-wide self-help group for the relatives concerned. To protect yourself from false pity and incompetent comments, the website is not public. However, there is an email address that can be used to contact the group. Since even a child with a one-sided anophthalamus cannot avoid numerous cosmetic operations, the parents, whose daughter or son is “only” affected on one side, are in the right place.