An ankyloglosson is a developmental disorder of the tongue that is already congenital. This results in an overgrown ligament of the tongue that affects the movements of the tongue.
What is ankyloglosson?
According to phonejust, the frenulum of the tongue is a muscular fold that is covered by mucous membrane. In some babies, the frenulum becomes too short, which in turn has a negative effect on tongue mobility.
The ankyloglosson is also known in medicine under the names ankyloglossum or ankyloglossia . This is a congenital tongue development disorder in which the frenulum linguae is fixed to the floor of the mouth. Because this disorder limits the movement of the tongue, the affected babies have difficulty breastfeeding.
In the further course there is a risk of disturbances in speaking and in making sounds. According to studies, ankyloglossone is responsible for difficulties in about 16 percent of all babies with breastfeeding problems. Official estimates assume four to ten percent of all infants.
In principle, however, the number of babies affected should be higher than stated in the specialist literature, because it was common in earlier times to breastfeed babies with a bottle. The baby is usually not hindered by ankyloglosson. Because more babies are now being breast-fed, the shortened tongue frenulum was found more frequently.
Causes
The frenulum of the tongue is a muscular fold that is covered by mucous membrane. It creates a connection between the lower surface of the tongue and the floor of the mouth. In some babies, the frenulum becomes too short, which in turn has a negative effect on tongue mobility.
Ankyloglosson is already congenital. It is unclear what causes this developmental disorder of the tongue. The lingual frenulum plays an important role in babies’ ability to absorb milk from their mother’s breast. To do this, it is necessary to stretch out the tongue over the lower jaw ridge.
The baby then makes massaging movements with his tongue that push the milk out of the breast. However, if the tongue is firmly anchored in the floor of the mouth, the infant cannot lift it above the lower lip. As a result, the buffer between the groin of the jaw is missing and the baby only takes the nipple in its mouth.
The mother again has the feeling that her child is about to bite. It is not uncommon for her to have sore and painful nipples as a result. Because the baby is unable to perform the necessary undulating movements and there is no negative pressure, the milk can only flow poorly.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
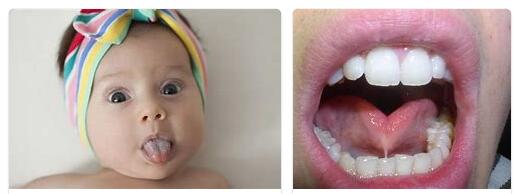
Ankyloglosson is noticeable through a tongue that is too short and too thick. When the tongue is stuck out, a heart-shaped contour emerges. In addition, the mobility of the tongue suffers from ankyloglossia. So it is not possible to slide the tongue over the lower teeth or the lower lip.
In addition, there are restrictions on movements in the upper or lateral direction. The affected babies therefore have problems breastfeeding. This means they cannot put their tongue on and keep slipping while breastfeeding. Because of this, they want to be fed constantly.
In addition, the infants gain weight only slowly and often suffer from colicky pain . Ankyloglosson can also exist if not all of the symptoms described occur. Sometimes, however, these signs also show up when there is no shortened tongue frenulum.
Diagnosis & course
The diagnosis of ankyloglosson can be made as part of the U1 examination, which takes place immediately after the birth. To do this, a doctor or midwife will put a finger in the baby’s mouth and examine the tongue and roof of the mouth. However, ankyloglossia cannot be discovered immediately in every baby.
It is not uncommon for the malformation to become apparent only when problems arise with breastfeeding. Sometimes ankyloglosson is only noticeable when the child is two or three years old and has language difficulties. To determine whether the ligament of the tongue is shortened, the pediatrician uses a spatula to slide the base of the tongue from side to side.
If this movement cannot be carried out, there is an ankyloglosson. Ankyloglossia usually takes a positive course. The treatment in which the ligament of the tongue is severed is considered to be simple. Complications are usually not to be feared.
Complications
The ankyloglosson refers to the ligament of the tongue that has been shortened from birth. About five percent of all infants are affected. If a newborn is diagnosed with this diagnosis, it is advisable to treat the ankyloglossone quickly. Unnecessary complications that would otherwise have a significant impact on language acquisition and the child’s healthy development are avoided.
The shortened ankyloglosson affects the mobility of the tongue. In addition, breastfeeding the baby proves to be impractical. It cannot suck or swallow properly. The infant is threatened with colicky pain and rapid weight loss. If the ankyloglosson is not corrected, the position of the tongue changes completely and there is also the risk of misaligned teeth.
Likewise, the toddler cannot utter many sounds in the later course of his language ability. The tongue seems rigid. Mouth breathing often occurs as a result, which increases the susceptibility to infection. If the undesirable development is less pronounced, an intervention should still be carried out before school starts.
As you grow up, unpleasant problems can arise with braces, tongue piercing or kissing at the latest. If the person concerned has an accident or premature tooth loss, fitting a dental prosthesis can be difficult. The surgical intervention to correct the misalignment of the tongue ligament, on the other hand, is risk-free.
When should you go to the doctor?
Ankyloglossone does not necessarily have to be treated by a doctor. However, if the shortened frenulum of the tongue causes pain or other discomfort, medical help is needed. Parents should see a doctor if the child has problems breastfeeding and shows signs of colicky pain. If the affected infant eats too little food due to the symptoms, the pediatrician must be informed. The doctor can usually diagnose the ankyloglosson unequivocally by examining the tongue and palate and suggest an operation.
Sometimes, however, the shortened frenulum of the tongue is not noticed until the second or third year of life. See a doctor if the child has trouble speaking or shows signs of pain. At the latest when misaligned teeth are found, the child should be taken to the doctor. In less severe cases, the affected child can have the ankyloglosson clarified later in life. This is necessary, for example, if kissing, tongue piercing or braces cause problems. The frenulum can be corrected at any age and is usually risk-free and painless.
Treatment & Therapy
The treatment of an ankyloglosson consists of a surgical severing of the tongue ligament that has grown into it. The procedure is considered useful if the baby is suffering from breastfeeding problems and speech disorders are threatened. In other cases, however, the procedure is only carried out if the affected child actually has language problems.
Ankyloglossone does not always require therapy. This can be omitted if the tongue frenulum does not cause any problems. Ultimately, the extent of the complaint decides whether to treat it. In the opinion of experts, however, this should be done early if the tongue can only be moved to a limited extent.
A surgical procedure on the frenulum takes about 20 to 25 minutes. If necessary, the child is given a brief general anesthetic . If this leads to risks, the operation must be postponed. As part of the procedure, the doctor first pulls the tongue upwards. The next step is to cut the ribbon with a short cut. The wound is then sutured with threads that dissolve by themselves.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis for ankyloglosson is very good. In a short surgical procedure that only takes a few minutes, the ligament of the tongue that has grown is severed under general anesthesia. The wound in the mouth is then adequately treated so that it can heal completely within a few days. The patient is then normally considered to be symptom-free and permanently cured.
If complications arise beforehand, the healing process can be delayed. In the event of a drastic weight loss, this must first be gradually built up again in the coming months after the operation. Depending on the child’s personality and behavior, this can take some time, a lot of patience and perseverance. If the child has developed fears , these have to be broken down and new trust in eating has to be built up.
In rare cases, general anesthesia can lead to secondary symptoms. These also prolong the healing process. There may be intolerance reactions due to the medication given or sleep disorders may set in. The symptoms are temporary in most patients. Most of the time, they are completely healed after a few weeks. Breastfeeding difficulties can also be expected after the corrective intervention. The prognosis for possible breastfeeding after the surgical procedure are less optimistic. The infant is therefore switched to substitute products very early on.
Prevention
It is not possible to prevent ankyloglosson. It is a congenital developmental disorder.
Aftercare
Follow-up care options are not available to those affected by ankyloglosson. However, these are also not necessary, as the disease can be treated with a surgical procedure, whereby there are usually no particular complications or other difficulties. The disease can be completely treated by the surgical procedure, whereby the life expectancy of the patient is not negatively affected.
After the procedure, the person affected must rest and take care of their body. A full recovery usually occurs quickly, so that a long stay in the hospital is not necessary. The threads also usually dissolve by themselves and do not have to be pulled.
Since the ankyloglosson is usually removed at a young age, the parents often try to calm the child down and take away the fear of the operation. Since the complaints can also lead to psychological upset or depression, discussions with parents and relatives are very useful. Contact with other sufferers of ankyloglosson can also have a positive effect on the course of the disease. The earlier the disease is treated, the better complications can be avoided.
You can do that yourself
Ankyloglosson can now be treated easily and without complications. After the surgical severing of the tongue ligament, patients should follow the doctor’s instructions. The doctor will recommend an adapted diet without irritating or spicy foods. Caffeine, alcohol and nicotine should also be avoided initially so that the surgical wound does not become infected. An appropriate diet is also recommended before the procedure. Should problems arise after the operation, the doctor must be informed.
Parents who find ankyloglosson in their child should have it removed as early as the newborn if possible. If language problems have already developed, these must be corrected with the help of a speech therapist . Since the removal of ankyloglosson is a routine procedure, no further measures are necessary. After the procedure, rest and rest for a few days. Follow-up care is limited to a check-up by the family doctor , who will check the site of the operation.
In the event of pain or swelling, general measures such as applying a cold pack can help. In the first few days, care should be taken with oral hygiene so that the wound is not injured and accidentally opened.